Please support the blog via Swish (Sweden), MobilePay (Finland) or Wise.
Human history extends at least six million years back in time. One theory points to the Tugen hills between Lake Victoria (Tanzania, Uganda, Kenya) and Lake Turkana (Kenya, Ethiopia) as the place where our early ancestors - the Orrorins - lived (Curnoe, 2016; Patterson et al. 2006; Pickford och Senut, 2001; Pickford, 2006). Like other animals, the Orrorin's hade no higher cognitive capacity like probabalistic logic, or creative thinking which are subsets to the modern minde. This implies that perception and intuition interacted with emotions and motivation, so called PRIMES (Buck, 1985), in an instant manner.
Findings suggest that our ancestors, the Australopithecus afarensis, a.k.a. Lucy, ate bone marrow some 3.5 million years before the present (Mann, 2018; McPherron et al. 2010; Thompson et al. 2019). This new nutrient dense diet started a process that reduced their guts, and expanded their brain (Aiello and Wheeler, 1995).
2.8 million years before the present, our genus - Homo - existed. Their brains were 50% larger compared to Lucy's kind (Kimbel och Villmoare, 2016; Villmoare, 2018; Villmoare et al. 2015).
Soon after, the climate changed when Neogene (23 - 2.58 mya) was replaced by Quaternary (2.58 - ), and Pliocene (5.33 - 2.58 mya) by Pleistocene (2.58 -). Findings show that our ancestors at that time ate meat (Pobiner, 2013, 2016).
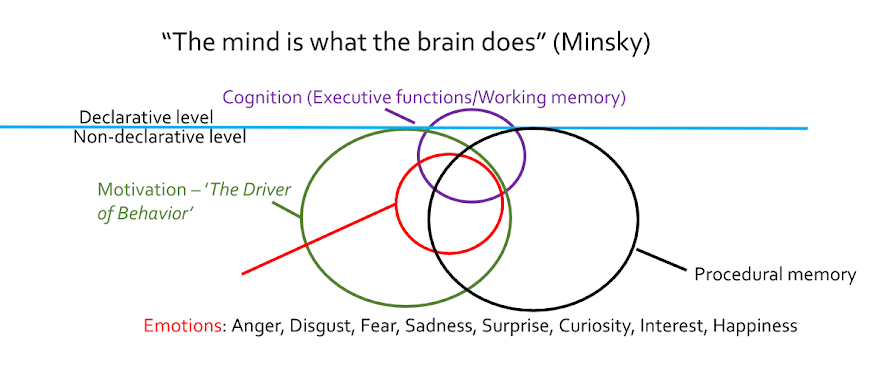
Slowly, our ancestors turned into cognitive beings, adding social cognition, symbolic thinking, and executive functions (Ardila, 2008, Ardila et al. 2018; Adornetti, 2016; Coolidge and Wynn, 2018; Diamond, 2013; Diamond and Lee, 2011; Österberg, 2004). That include a unique conscious to suppress impulse in favor of playing with ideas and run them forward in time - prospective thinking (Barkley, 2001; Gilbert and Wilson, 2007; Kaku, 2014; Liu et al. 2017; Locke et al. 1981; Locke and Latham, 2002; Suddendorf et al. 2018; Szpunar et al. 2014).
When an intentional prospect, that is, a goal, is presented the consequence is a problem - the difference between the current state and the goal state. If a problem is familiar: current knowledge and strategies can be applied. On the other hand, if the problem is unfamiliar: new knowledge and strategies have to be formed, i.e., learning and/or creative thinking is needed (Duncker, 1945).
Read: Allen Newell (1979) Duncker on Thinking: An Inquiry into Progress in Cognition.
- An organization exists for the purpose of attaining a common goal.
- The purpose of goal-setting is to influence performance, learning, and creativity for problem solving.
- Goal setting is the work of the leader.
- the unknown person who assigned the goal that led to the erection of Göbekli Tepe
- Filippo Brunelleschis (1377-1446) erection of the self-supporting dome of Florence Cathedral (the construction of the main building was the work of Arnolfo di Cambio (1240 – 1300/1310))
- John F Kennedy's two addresses about putting a man on the moon (1, 2).
Please support the blog via Swish (Sverige) eller MobilePay (Finland).
More about my expertis:
Executive coaching for CEOs/managers and workshops to facilitate Organizational Performance, Learning, and Creativity for Problem Solving | Lectures: Nutrition for physical and mental health | Course/lecture: children's emotional and social adjustment and cognitive development | Language training - Swedish | Academy Competency | CV | Teaching skills and experience | Summary of research project | Instagram | Linkedin | YouTube-channel | TikTok | Twitter
No comments:
Post a Comment